Class information for: |
Basic class information |
| ID | Publications | Average number of references |
Avg. shr. active ref. in WoS |
|---|---|---|---|
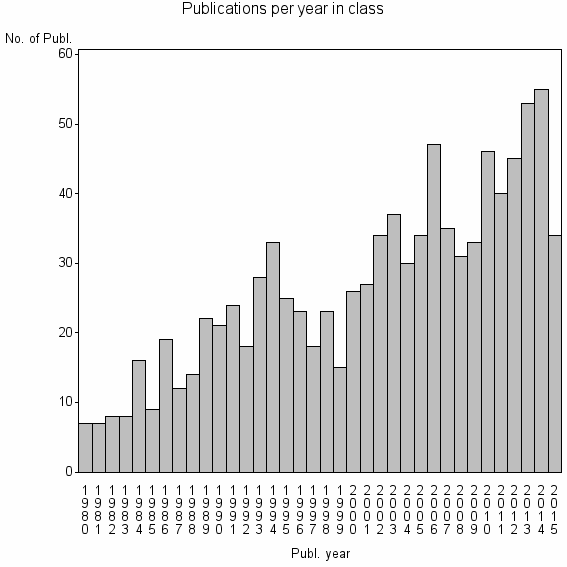
| 10906 | 957 | 31.0 | 61% |
Classes in level above (level 2) |
| ID, lev. above |
Publications | Label for level above |
|---|---|---|
| 2485 | 3480 | NON INVASIVE VENTILATION//POST POLIO SYNDROME//NONINVASIVE MECHANICAL VENTILATION |
Terms with highest relevance score |
| Rank | Term | Type of term | Relevance score (tfidf) |
Class's shr. of term's tot. occurrences |
Shr. of publ. in class containing term |
Num. of publ. in class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MECHANICAL INSUFFLATION EXSUFFLATION | Author keyword | 49 | 82% | 3% | 28 |
| 2 | PEAK COUGH FLOW | Author keyword | 38 | 93% | 1% | 14 |
| 3 | EXSUFFLATION | Author keyword | 17 | 75% | 1% | 12 |
| 4 | ASSISTED COUGH | Author keyword | 15 | 82% | 1% | 9 |
| 5 | NEUROMUSCULAR DISEASE | Author keyword | 15 | 17% | 8% | 81 |
| 6 | MAXIMUM INSUFFLATION CAPACITY | Author keyword | 15 | 88% | 1% | 7 |
| 7 | HOME MECHANICAL VENTILATION | Author keyword | 13 | 32% | 4% | 34 |
| 8 | TECHNOLOGY DEPENDENT CHILDREN | Author keyword | 12 | 75% | 1% | 9 |
| 9 | TUSSOMETRY | Author keyword | 9 | 83% | 1% | 5 |
| 10 | TECHNOLOGY DEPENDENT | Author keyword | 8 | 60% | 1% | 9 |
Web of Science journal categories |
Author Key Words |
| Rank | Web of Science journal category | Relevance score (tfidf) |
Class's shr. of term's tot. occurrences |
Shr. of publ. in class containing term |
Num. of publ. in class |
LCSH search | Wikipedia search |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MECHANICAL INSUFFLATION EXSUFFLATION | 49 | 82% | 3% | 28 | Search MECHANICAL+INSUFFLATION+EXSUFFLATION | Search MECHANICAL+INSUFFLATION+EXSUFFLATION |
| 2 | PEAK COUGH FLOW | 38 | 93% | 1% | 14 | Search PEAK+COUGH+FLOW | Search PEAK+COUGH+FLOW |
| 3 | EXSUFFLATION | 17 | 75% | 1% | 12 | Search EXSUFFLATION | Search EXSUFFLATION |
| 4 | ASSISTED COUGH | 15 | 82% | 1% | 9 | Search ASSISTED+COUGH | Search ASSISTED+COUGH |
| 5 | NEUROMUSCULAR DISEASE | 15 | 17% | 8% | 81 | Search NEUROMUSCULAR+DISEASE | Search NEUROMUSCULAR+DISEASE |
| 6 | MAXIMUM INSUFFLATION CAPACITY | 15 | 88% | 1% | 7 | Search MAXIMUM+INSUFFLATION+CAPACITY | Search MAXIMUM+INSUFFLATION+CAPACITY |
| 7 | HOME MECHANICAL VENTILATION | 13 | 32% | 4% | 34 | Search HOME+MECHANICAL+VENTILATION | Search HOME+MECHANICAL+VENTILATION |
| 8 | TECHNOLOGY DEPENDENT CHILDREN | 12 | 75% | 1% | 9 | Search TECHNOLOGY+DEPENDENT+CHILDREN | Search TECHNOLOGY+DEPENDENT+CHILDREN |
| 9 | TUSSOMETRY | 9 | 83% | 1% | 5 | Search TUSSOMETRY | Search TUSSOMETRY |
| 10 | TECHNOLOGY DEPENDENT | 8 | 60% | 1% | 9 | Search TECHNOLOGY+DEPENDENT | Search TECHNOLOGY+DEPENDENT |
Key Words Plus |
| Rank | Web of Science journal category | Relevance score (tfidf) |
Class's shr. of term's tot. occurrences |
Shr. of publ. in class containing term |
Num. of publ. in class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MECHANICAL INSUFFLATION EXSUFFLATION | 49 | 64% | 5% | 48 |
| 2 | COUGH AUGMENTATION | 31 | 92% | 1% | 12 |
| 3 | NEUROMUSCULAR DISEASE | 30 | 24% | 11% | 108 |
| 4 | RESPIRATORY MUSCLE WEAKNESS | 26 | 47% | 4% | 41 |
| 5 | PULMONARY MORBIDITY | 15 | 45% | 3% | 25 |
| 6 | ASSISTED CHILDREN | 14 | 100% | 1% | 7 |
| 7 | MECHANICAL INSUFFLATION | 12 | 75% | 1% | 9 |
| 8 | NASAL VENTILATION | 12 | 23% | 5% | 46 |
| 9 | VENTILATOR DEPENDENT CHILDREN | 12 | 86% | 1% | 6 |
| 10 | DAYTIME PREDICTORS | 11 | 78% | 1% | 7 |
Journals |
Reviews |
| Title | Publ. year | Cit. | Active references | % act. ref. to same field |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Changing Trends in the Management of End-Stage Neuromuscular Respiratory Muscle Failure Recommendations of an International Consensus | 2013 | 11 | 100 | 63% |
| Respiratory care of the patient with duchenne muscular dystrophy - ATS Consensus Statement | 2004 | 195 | 88 | 55% |
| The use of mechanical ventilation is appropriate in children with genetically proven spinal muscular atrophy type I: the motion for | 2008 | 22 | 11 | 100% |
| Neuromuscular disease and respiratory physiology in children: Putting lung function into perspective | 2014 | 3 | 59 | 59% |
| Chronic respiratory care for neuromuscular diseases in adults | 2009 | 32 | 67 | 42% |
| Noninvasive respiratory management of high level spinal cord injury | 2012 | 6 | 23 | 70% |
| Airway clearance in neuromuscular weakness | 2009 | 8 | 28 | 89% |
| Respiratory management of the infant with type 1 spinal muscular atrophy | 2005 | 26 | 4 | 100% |
| Implementation of "the consensus statement for the standard of care in spinal muscular atrophy" when applied to infants with severe type 1 SMA in the UK | 2010 | 11 | 20 | 65% |
| The use of invasive ventilation is appropriate in children with genetically proven spinal muscular atrophy type I: the motion against | 2008 | 18 | 18 | 56% |
Address terms |
| Rank | Address term | Relevance score (tfidf) |
Class's shr. of term's tot. occurrences |
Shr. of publ. in class containing term |
Num. of publ. in class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CLIN SLEEP BREATHING | 7 | 67% | 0.6% | 6 |
| 2 | UNIV HOSP S JOAO | 6 | 100% | 0.4% | 4 |
| 3 | UNITE MIXTE RECH 805 | 3 | 100% | 0.3% | 3 |
| 4 | LUNG FUNCT VENTILAT UNIT | 3 | 60% | 0.3% | 3 |
| 5 | ABT PNEUMOL LAF BEATMUNGSMED | 2 | 67% | 0.2% | 2 |
| 6 | LIFETIME SERV | 2 | 67% | 0.2% | 2 |
| 7 | P REHABIL SERV | 2 | 67% | 0.2% | 2 |
| 8 | PLUNKETT | 2 | 67% | 0.2% | 2 |
| 9 | GEN PEDIAT NEUROPEDIAT | 2 | 50% | 0.3% | 3 |
| 10 | SLEEP VENTILAT UNIT | 2 | 21% | 0.8% | 8 |
Related classes at same level (level 1) |
| Rank | Relatedness score | Related classes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.0000262400 | NON INVASIVE VENTILATION//NONINVASIVE POSITIVE PRESSURE VENTILATION//ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE |
| 2 | 0.0000199524 | DUCHENNE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY//NORTH STAR AMBULATORY ASSESSMENT//REG HABILITAT |
| 3 | 0.0000155608 | DIAPHRAGM PACING//CROSSED PHRENIC PHENOMENON//LONG TERM FACILITATION |
| 4 | 0.0000139322 | AMYOTROPHIC LATERAL SCLEROSIS//AMYOTROPHIC LATERAL SCLEROSIS AND FRONTOTEMPORAL DEGENERATION//MOTOR NEURON DISEASE |
| 5 | 0.0000111333 | NEUROMUSCULAR SCOLIOSIS//KYPHECTOMY//PELVIC OBLIQUITY |
| 6 | 0.0000092293 | RIGID SPINE SYNDROME//RIGID SPINE//EMERINOPATHY |
| 7 | 0.0000086141 | CHEST PHYSIOTHERAPY//ENDOTRACHEAL SUCTIONING//AUTOGENIC DRAINAGE |
| 8 | 0.0000076585 | PIERRE ROBIN SEQUENCE//GLOSSOPTOSIS//TONGUE LIP ADHESION |
| 9 | 0.0000076143 | RESPIRATORY MUSCLES//CARDIO P PHYSIOL//CHEST SERV |
| 10 | 0.0000072911 | FAMILY CENTRED CARE//DOCTOR PARENT CHILD COMMUNICATION//PAEDIATRIC NURSING |