In this course, there will be live lectures, recorded lectures and exercises. During the exercises we use pen/paper and computer to understand the basics of thermodynamic modelling.
MH2057 Computational Thermodynamics 7.5 credits
In this course, you will get to know how to model the thermodynamics of different chemical system and to use the software Thermo-Calc.
Information per course offering
Information for Autumn 2026 Start 24 Aug 2026 programme students
- Course location
KTH Campus
- Duration
- 24 Aug 2026 - 23 Oct 2026
- Periods
Autumn 2026: P1 (7.5 hp)
- Pace of study
50%
- Application code
10901
- Form of study
Normal Daytime
- Language of instruction
English
- Course memo
- Course memo is not published
- Number of places
Min: 1
- Target group
- Open for application for CMATD3 and TTMVM1. Elective for all programs, provided that the course can be included in the program.
- Planned modular schedule
- [object Object]
- Schedule
- Schedule is not published
- Part of programme
Degree Programme in Materials Design and Engineering, year 3, INE, Mandatory
Degree Programme in Materials Design and Engineering, year 3, MMM, Mandatory
Degree Programme in Materials Design and Engineering, year 3, TMV, Mandatory
Degree Programme in Materials Design and Engineering, year 3, NTE, Mandatory
Degree Programme in Materials Design and Engineering, year 3, PRM, Mandatory
Degree Programme in Materials Design and Engineering, year 3, TEMB, Mandatory
Master's Programme, Engineering Materials Science, year 1, Mandatory
Degree Programme in Materials Design and Engineering, year 3, Mandatory
Contact
Course syllabus as PDF
Please note: all information from the Course syllabus is available on this page in an accessible format.
Course syllabus MH2057 (Autumn 2024–)Content and learning outcomes
Course disposition
Course contents
- Thermodynamic models for solid phases, liquids and gas phase
- Modelling of solid substitutional and interstitial solution, carbides, oxides and intermetallic phases
- Modelling of metallic melt systems and slags
- The connection between Gibbs energy and phase diagrams
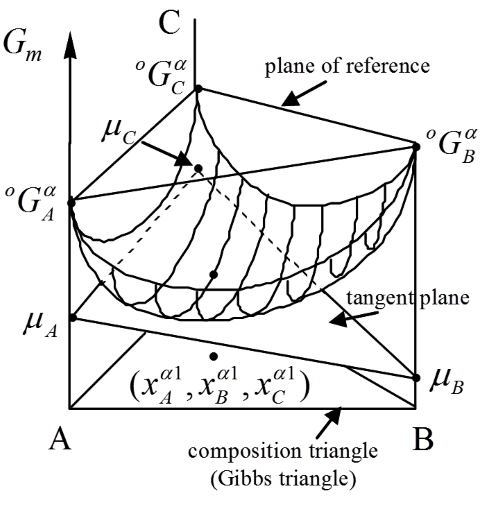
- Reading of quantities such as chemical potential, driving forces etc from molar Gibbs energy diagram
- Reference state and change of reference state and change of components
- Phase diagrams and equilibria
- Computer calculations of equilibria, phase diagrams, driving forces etc
- Nomenclature of crystal structures
- Introduction to the Calphad methodology
Intended learning outcomes
After passing the course, the student should be able to:
- Explain important concepts in thermodynamic modelling
- Use thermodynamic relationships for solution phases (solid phases, liquids and gas phase).
- Model these phases with simple models and with sub-lattice formalism (Compound Energy Formalism).
- Illustrate relationships between thermodynamic relations, Gibbs energy and phase diagrams.
- Carry out analytical and numerical calculations of thermodynamic problems.
Literature and preparations
Specific prerequisites
For CMATD, at least 90 higher education credits in the main field of study Technology from programme syllabus for year 1-3.
Literature
Examination and completion
Grading scale
Examination
- INL1 - Assignment, 3.5 credits, grading scale: P, F
- undefined - undefined, undefined, grading scale: undefined
Based on recommendation from KTH’s coordinator for disabilities, the examiner will decide how to adapt an examination for students with documented disability.
The examiner may apply another examination format when re-examining individual students.
If the course is discontinued, students may request to be examined during the following two academic years.
Examiner
Ethical approach
- All members of a group are responsible for the group's work.
- In any assessment, every student shall honestly disclose any help received and sources used.
- In an oral assessment, every student shall be able to present and answer questions about the entire assignment and solution.