The focus of the course is on machine learning methods and algorithms for communication protocols of Internet of Things (IoT). The course starts with an introduction of applications of network architecture. Thereafter, methods for communication protocols are treated and how these methods can be applied in the design of important aspects of the communication protocol stack. The course analyses machine learning algorithms that can be run on IoT systems, where data and calculations are distributed.
EP271V Internet of Things and Artificial Intelligence 7.5 credits
This course will be discontinued.
Decision to discontinue this course:
The course will be discontinued at the end of autumn 2027 according to faculty board decision: HS-2025-2307.
Decision date: 2025-10-07
The course will be given for the last time in autumn 2025. The last opportunity for examination in the course will be given in autumn 2027.
Contact the examiner to be examined during the discontinuation period
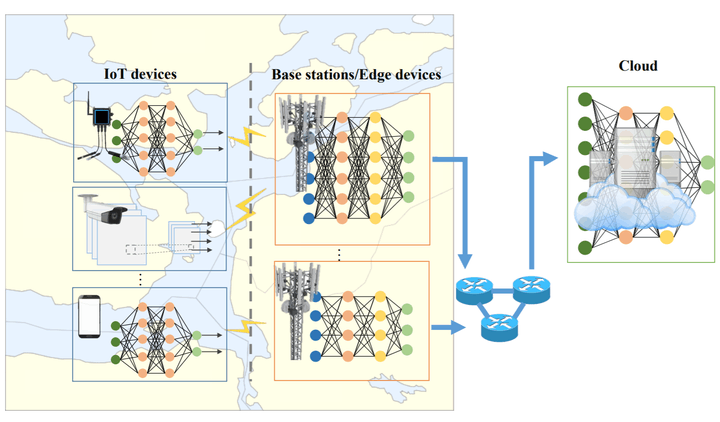
The Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) are technologies that make “the world of everything connected” because they can connect physical objects, people, or infrastructure, especially thanks to wireless communications. IoT and AI allow us to gather data, make data analysis, and ultimately take some automatic decisions. We will use IoT and AI in the digitalized world, where vehicles will drive without human drivers, and energy and water resources will be distributed much more efficiently than today. This course gives an overview on the most important aspects of wireless networking and machine learning for AI over IoT.
Information per course offering
Course offerings are missing for current or upcoming semesters.
Course syllabus as PDF
Please note: all information from the Course syllabus is available on this page in an accessible format.
Course syllabus EP271V (Autumn 2025–)Content and learning outcomes
Course contents
Intended learning outcomes
After passing the course, the student should be able to:
- give an account of the central tools in communication technology for Internet of Things (IoT)
- design IoT systems
- give an account of central machine learning methods for IoT
- design machine learning methods for IoT systems
in order to:
- understand and explain which design options there are for a specific communication system
- be able to provide arguments for which type of performance that should be prioritised in the design of IoT systems and machine learning methods
- understand and explain machine learning design options for specific communication systems.
Literature and preparations
Specific prerequisites
- In total 180 higher education credits of which at least 90 higher education credits in electrical engineering, engineering physics or technical
- mathematics.
- Knowledge in one variable calculus, 6 higher education credits.
- Knowledge in computer communication, 6 higher education credits.
- Knowledge in probability theory, 6 higher education credits.
- The upper secondary course English B/6
Literature
Examination and completion
Grading scale
Examination
- PRO1 - Project work, 1.5 credits, grading scale: A, B, C, D, E, FX, F
- LAB1 - Laboratory task, 2.0 credits, grading scale: A, B, C, D, E, FX, F
- LAB2 - Laboratory task, 2.0 credits, grading scale: A, B, C, D, E, FX, F
- LAB3 - Laboratory task, 2.0 credits, grading scale: A, B, C, D, E, FX, F
Based on recommendation from KTH’s coordinator for disabilities, the examiner will decide how to adapt an examination for students with documented disability.
The examiner may apply another examination format when re-examining individual students.
If the course is discontinued, students may request to be examined during the following two academic years.
Examiner
Ethical approach
- All members of a group are responsible for the group's work.
- In any assessment, every student shall honestly disclose any help received and sources used.
- In an oral assessment, every student shall be able to present and answer questions about the entire assignment and solution.