Translations and simple rotations, the notion of invariance in physics, the definition of space and time in Newtonian mechanics, Galileiinvarians, addition of velocitites in Newtonian mechanics, the concepts of inertial and rest frames of reference, Lorentz time transformation, the nature of light and speed, the Michelson-Morley experiment and Lorentzcontractionen, simultaneity, length contraction, the twin paradox, relativistic kinematics and relativistic reactions.
SI150V Introductory Relativity Theory 4.5 credits
This course will be discontinued.
Last planned examination: Spring 2026
Decision to discontinue this course:
No information inserted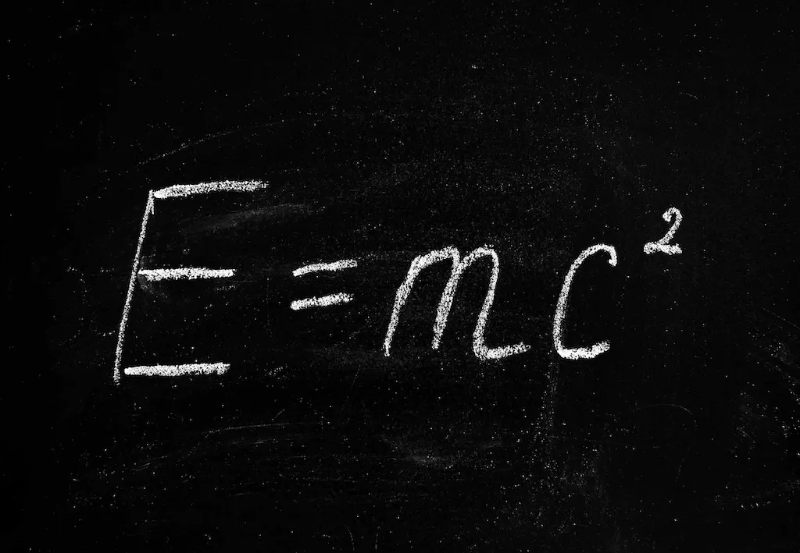
This is a web-based course that provides an introduction to the theory of relativity, which describes the dramatic way in which everyday concepts such as length, time and energy change when traveling at very high speeds, close to the speed of light. As an example, we will study how objects seem to shrink when they move close to the speed of light. Furthermore, we treat other known consequences of the theory of relativity such as the twin paradox, which deals with how the age of two twins is affected by one making a space trip at a very high speed. We will also derive the most famous equation in physics: E = mc2, which describes the relationship between energy and mass. During the course you will see examples that the theory of relativity is not only an abstract theory. It is essential in the construction of modern particle accelerators, and even the modern navigation system GPS relies on the theory of relativity.
Information per course offering
Course offerings are missing for current or upcoming semesters.
Course syllabus as PDF
Please note: all information from the Course syllabus is available on this page in an accessible format.
Course syllabus SI150V (Autumn 2023–)Content and learning outcomes
Course contents
Intended learning outcomes
After completing the course you should be familiar with basic concepts in both the theory of relativity and the mechanics prior to Einstein, for example, invariance and symmetry, observers and reference frames. You should have gained insight into the contradictions between the Newtonian mechanics and Maxwell's equations that led to the revolution of relativity. You should be able to transform time and space between observer that move relative to each other and realize how these transformations lead to length contraction and tidsdiltation. Realize the connection between mass and energy to have insight in how relativistic phenomena are exploited in technological applications.
Literature and preparations
Specific prerequisites
Mathematics D/Mathematics C, Physics B/Physics 2 with the lowest grade passed.
Literature
Examination and completion
Grading scale
Examination
- INL1 - Assignment, 1.5 credits, grading scale: P, F
- INL2 - Assignment, 1.5 credits, grading scale: P, F
- INL3 - Assignment, 1.5 credits, grading scale: P, F
Based on recommendation from KTH’s coordinator for disabilities, the examiner will decide how to adapt an examination for students with documented disability.
The examiner may apply another examination format when re-examining individual students.
If the course is discontinued, students may request to be examined during the following two academic years.
Other requirements for final grade
Three completed sets of problems.
Examiner
Ethical approach
- All members of a group are responsible for the group's work.
- In any assessment, every student shall honestly disclose any help received and sources used.
- In an oral assessment, every student shall be able to present and answer questions about the entire assignment and solution.