Vehicles of today – propulsion and auxiliary systems.
Driving factors for environment friendly vehicles.
Propulsion and auxiliary systems for hybrid vehicles.
Generic components.
System concepts and simulations.
Development trends.
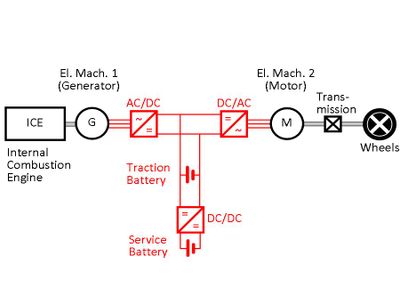
There is an increasing demand today to produce more environment friendly vehicles. The combustion engines of today can be improved but in the long run there has to be a change of technology. It will start with electric hybrid vehicles and a possible continuation is with vehicles driven by fuel cells. In parallel to this development the vehicles will contain more and more electrically supplied auxiliary systems.
The course covers both system and component aspects of the propulsion system, as well as the auxiliary systems. Emphasis is put on vehicles based on hybrid and/or fuel cells solutions.
KTH Campus
Autumn 2026: P2 (7.5 hp)
50%
11010
Normal Daytime
English
Min: 1
Please note: all information from the Course syllabus is available on this page in an accessible format.
Course syllabus EJ2410 (Spring 2019–)Vehicles of today – propulsion and auxiliary systems.
Driving factors for environment friendly vehicles.
Propulsion and auxiliary systems for hybrid vehicles.
Generic components.
System concepts and simulations.
Development trends.
Aim of the course is to give a broad insight into alternative solutions for conversion of primary energy to transport activity for road vehicles. Different types of fuel (fossile, bio, …), different types of conversion methods (FC, ICE, HEV), different topologies and auxiliary power systems are considered.
After completed course the student should be able to
Completed Bachelor's degree (180 higher education credits), or equivalent academic qualifications. Documented proficiency in English corresponding to English B.
Basic course on electrical engineering.
Kompendium i Hybrida fordonsdrivsystem, 2006. Kurspärm med projektbeskrivningar och laboration.
Based on recommendation from KTH’s coordinator for disabilities, the examiner will decide how to adapt an examination for students with documented disability.
The examiner may apply another examination format when re-examining individual students.
If the course is discontinued, students may request to be examined during the following two academic years.
One written examination. (TEN1; 4,5 credits)
Two assignments and one laboratory exercise. (PRO1; 3 credits).
N.B. EJ2410 Hybrid Vehicle Drives and EJ2440 Electric Transportation, contain to a certain extent the same material. It is therefore not possible to include both courses in the same degree.
In this course, the EECS code of honor applies, see:
http://www.kth.se/en/eecs/utbildning/hederskodex.