Research Activity on ICEs
Research at KTH Internal Combustion Engines division (2018-2021) and Unit of Mechatronics (2021-2023), the Department of Engineering Design & CCGEx
His research work on the internal combustion engines (ICEs) area was conducted at CCGEx. The project involves the following topics:
- Energy and exergy assessments of marine & HD truck engine systems.
- Combustion characterization associated with alcohol fuels.
- Aerothermodynamic analysis of gas-exchange systems.
- Measurement of exhaust pulses using fast flow measurement techniques.
Ph.D. defense presentation file: defense_ver02.pdf. The link for doctorial thesis in KTH diva: Exergy Evaluation of Engine Operations: Combustion Process to Exhaust Flow.
Combustion characterization and exhaust power assessment
RQ: Compared with gasoline, how do the different combustion patterns using bio-fuels affect the energy and exergy losses during combustion and the working potential of exhaust?
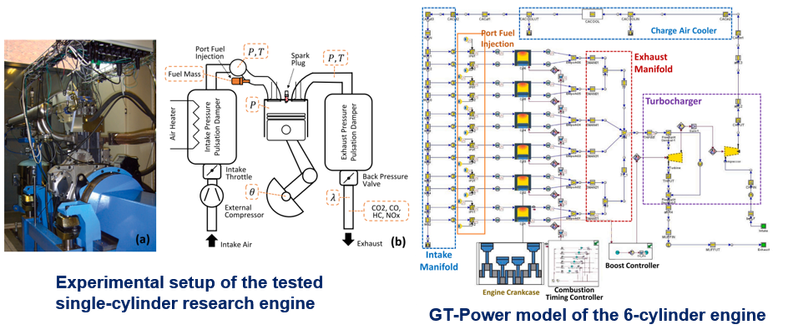
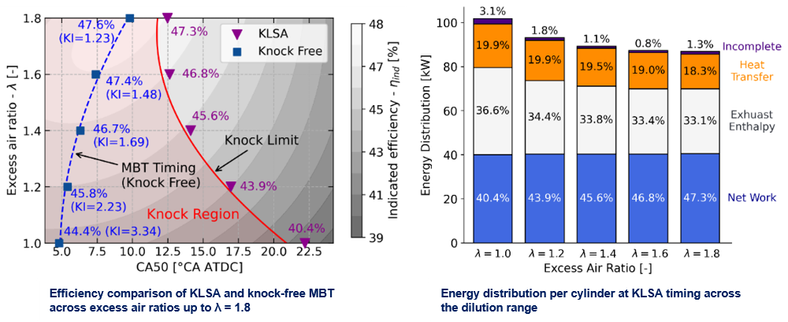
Based on an experiment on a single-cylinder research engine and GT-Power simulation, our study (2020.12 - 2021.03) contributes with a deeper understanding of the high-load performance of an ethanol-fueled heavy-duty SI engine using lean-burn combustion with excess air ratios up to 1.8. The engine’s thermal efficiency and combustion phasing are evaluated for knock limited operation and then compared to the theoretical optimum which is regardless of knock. Losses through heat transfer, exhaust flow, and incomplete combustion are quantified.
Energy and exergy distribution though engine systems
RQ: Where and to what extent do the engine exergy losses occur, associated with combustion, heat dissipation, and gas exchange?
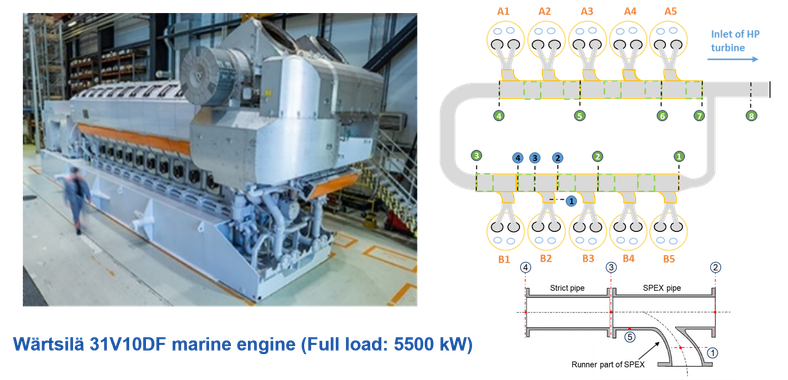
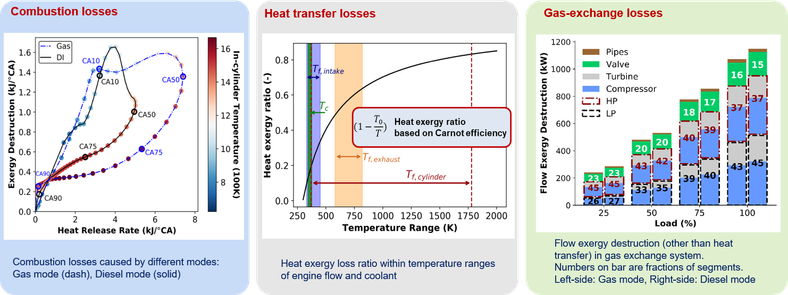
Energy and exergy analyses were conducted on two engine systems: a Scania D13 truck engine and a Wärtsilä 31DF marine engine. These analyses aimed to quantify the available energy losses of various components. Moreover, engine losses are characterized and quantified as three types: combustion, heat dissipation, and gas exchange losses. The results of the truck engine analysis were reported in a CCGEx internal report in 2019, while the analysis of the marine engine was published in 2020 (ICEF 2020-2956).
Pulsating flow measurement and exergy analysis
RQ: How to quantify exhaust pulsating flow enthalpy & exergy by using fast measurement techniques? In which approaches can we directly measure these flow variables in crank angle resolution?
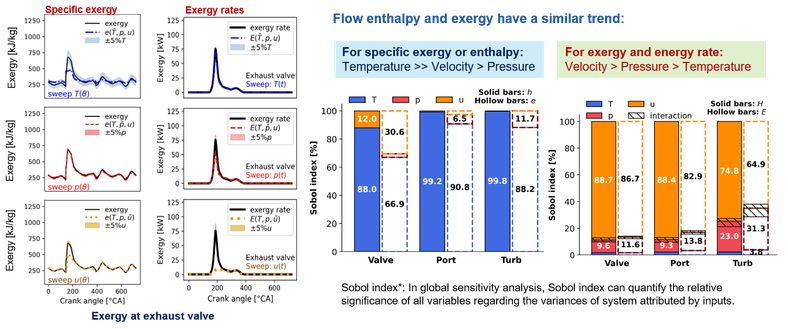
A sensitivity analysis-based method was applied to identify the significance of different flow parameters for the energy assessment of exhaust pulsation (2020). This study shows that the impacts of instantaneous flow velocity are important for exhaust energy quantification.
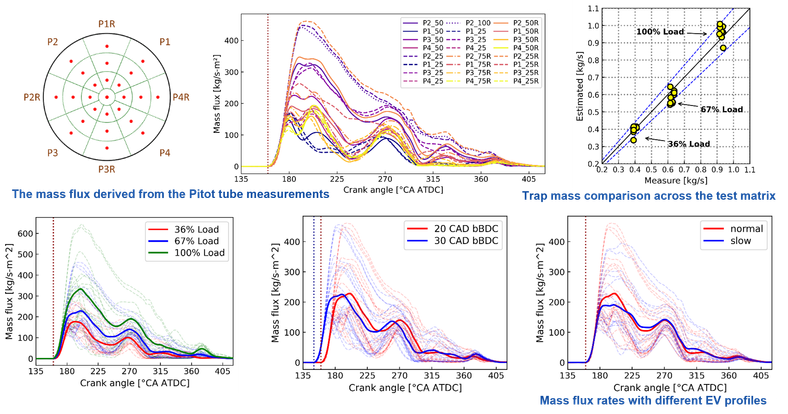
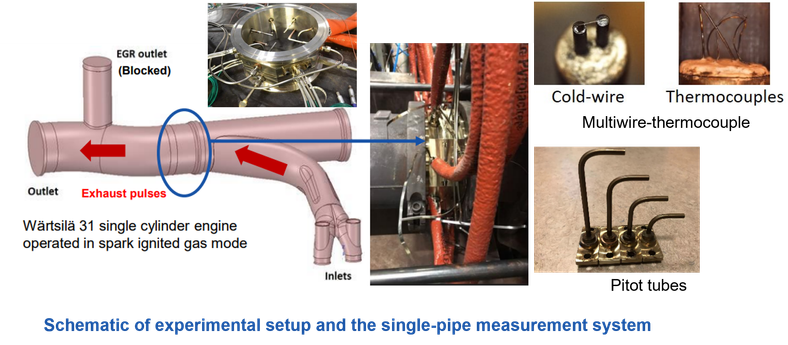
On-engine tests for measuring exhaust pulsation were completed in 2021 for a Scania truck engine and in 2022 for a Wärtsilä marine engine. A Pitot tube-based approach is adopted to measure exhaust mass flow pulsations, complemented by fast temperature measurements obtained using customized unsheathed thin-wire thermocouples.
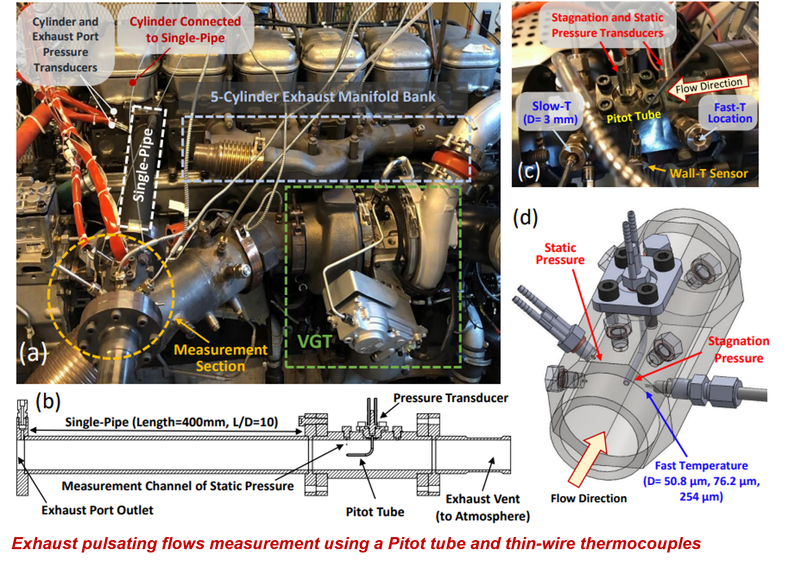
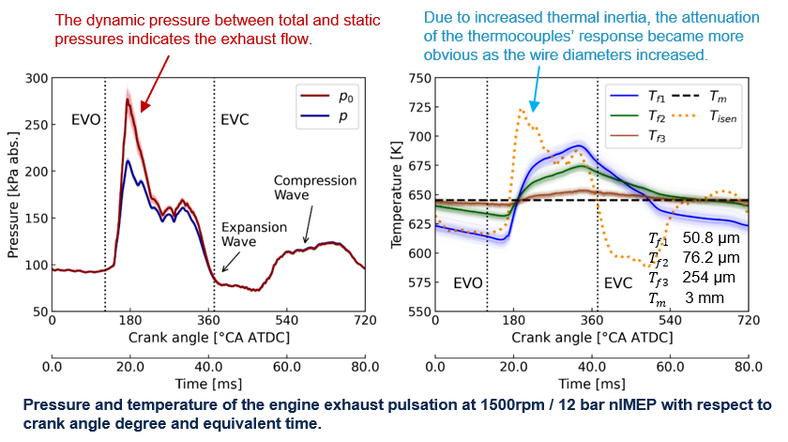
The research project on marine engine aims to measure and analyze the pulsating exhaust flow of a Wärtsilä single-cylinder research engine. The experimental campaign was conducted at the Wärtsilä Sustainable Technology Hub in Vaasa, Finland and consisted of two stages:
- Stage 1: Measurement and Data Analysis A measurement section was designed and implemented, incorporating multiple traversable Pitot tubes and thin-wire thermocouples to measure the total pressure and temperature of the exhaust pulses. The collected pulse data was analyzed under different engine operation conditions.
- Stage 2: Flow Field Reconstruction In addition to basic flow measurements and data analysis, a machine learning approach using the Expectation-Maximization (EM) algorithm was employed to estimate the time-varying flow field as a Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM). Furthermore, the GMM was optimized for the best configuration using the Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC).