|
Wettability of liquid iron on refractory oxides
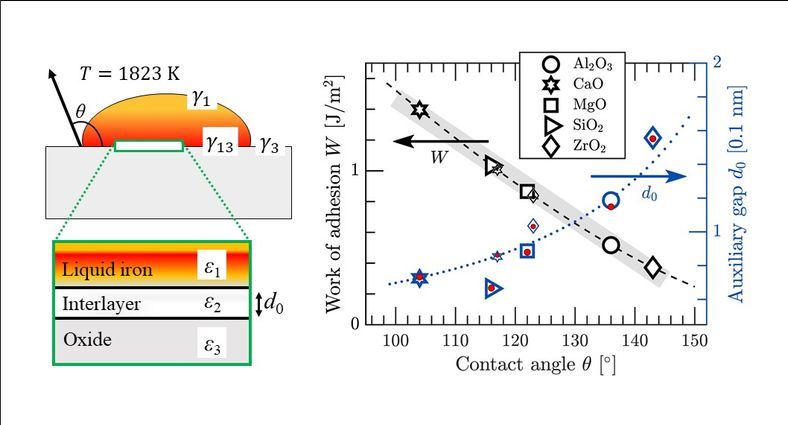
Refractory oxides serve dual roles in iron and steelmaking, both as components of surface materials in submerged entry nozzles and also as significant constituents of non-metallic inclusions in the melt. This paper presents a methodology for describing these interactions by combining the materials dielectric responses, computed within the density functional theory, with the Casimir-Lifshitz dispersion forces to generate the Hamaker constants. The approach provides a comprehensive understanding of the wettability of iron against these refractory oxides, revealing the complex relation between molecular and macroscopic properties. Our theoretically determined crystalline structures are confirmed by room-temperature X-ray diffraction, and the contact angles of liquid iron on the oxides are validated with a sessile drop system at the temperature 1823 K.
ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 17, 16173 (2025).
|
|
Group theoretically determination of irreducible representations
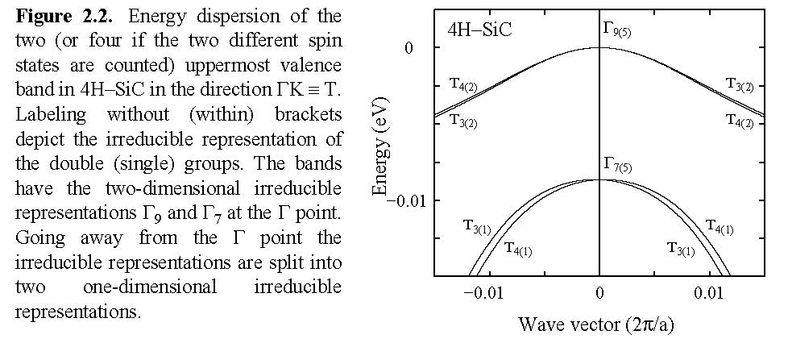
We present an open-source program to compute irreducible representations (IRs) of the electronic states of solids for all 230 space groups with an interface to the Vienna ab-initio Simulation Package (VASP). It originates from the WIEN2k irrep code that considers both single- and double-groups, analyses of time-reversal symmetry, and handles accidental degeneracies. The present code inherits those features but it has been extended to also be able to determine IRs of those special k-points for nonsymmorphic symmetries. In fact, it considers both type-I and type-II magnetic space groups. Labelling of the IRs is according to the convention of the BCS notation for the space groups.
Comput. Phys. Commun. 261, 107760 (2021).
Figure below is from PhD thesis, ISBN 91-7219-442-1 (UniTryck, Linköping, 1999).
|
|
Full-range spectroscopy of nanoparticles without light
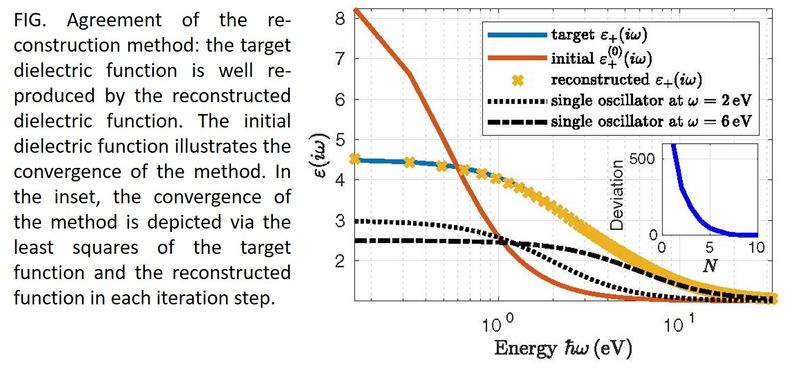
Along with total energies, electronic structure, and the lattice dynamics, the dielectric response function is the most fundamental property of a material. Experimentally, several different spectroscopy techniques are required to measure the dielectric function over the range of the electromagnetic spectrum, and that implies systematic errors. We have introduced a reconstruction method to extract the dielectric function for the full spectrum from established Casimir force experiments by altering the mixture of an intermediate liquid. Moreover, by combining various measured datasets of room temperature and ice-cold water we have generated a very reasonable empirical description of the dielectric function of water.
Phys. Rev. Appl. 13, 014025 (2020).
J. Phys. Chem. B 124, 3103 (2020).
|