Carbides Engineering
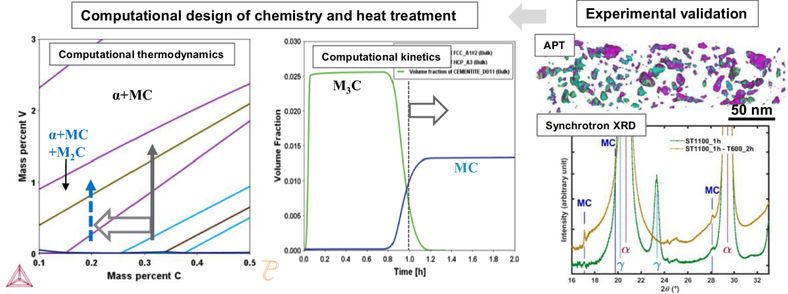
Figure 1. Carbides precipitation engineering using computatational thermodynamics and kinetics for high performance stool steels, validated by advanced characterization.
Cr, Mo, and V are widely used as alloying elements for carbon steels, especially tool steels and heat resistant steels, to increase hardenability, hardness, thermal stability,etc. They can potentially form carbide phases of V-rich MC, Mo-rich M2C and M6C, Cr-rich M7C3 and M23C6, etc., except for Fe-rich metastable carbides, depending on the chemical composition and process conditions. In our first works, mulitple carbides precipitation (tao-zhou-et-al-2020.pdf) and mechanical properties (tao-zhou-et-al-2020_2.pdf) of a high-performance tool steel were investigated, and it was found that coarse types of carbides were the dominant secondary phases at the tempering conditions, which is not ideal for the optimal performance. Therefore, carbides precipitation engineering were carried out to tailor the carbides precipitation using computational thermodynamics and kinetics (tao-zhou-et-al-2023.pdf) to achieve the precipitation of high number density of merely fine types of precipitates, as we know from open literature that the fine carbides precipitation has the merits of high precipitation strengthening, weak effects on toughness (also allowing the reduction in carbon content to improve toughness), H trapping for improved resistance to hydrogen embrittlement, higher thermal stability, increasing creep performance,etc.