Visa version
Visa
< föregående
|
nästa >
Jämför
< föregående
|
nästa >
Detailed instructions
This is a research exercise, so you should look outside the course material for further information. Books, journals, newspapers and internet, as well as personal and email communication with industry or academic experts are acceptable references. Reading reports from operational wind farms can help you understand the choices that have to be done. Complete tasks A – E, but also include anything you consider important and / or interesting for an investor, and stay within the page limit.
Task A: Analysis of Available Wind Turbine Technology
Instructions
-
Compare the technical designs of four wind turbines from different wind turbine manufacturers. You can choose any turbines within the wind turbine rating limits defined for your team.
-
Discuss the main features of the wind turbines, e.g. reactive power and fault ride through capabilities, power curves, weight etc., if available. Also discuss different foundation options and other issues related to the installation, e.g. issues related to the location.
-
Choose two turbine models for further examination, and explain your reasons for choosing them.
Details from the comparison should be summarised within one table, and include a discussion of not more than two pages of text.
Hints
Some wind turbine models can be found at
Task B: Wind Data Analysis
Instructions
-
Siting:
-
Nominate a possible location in the world that fits with the requirements for your group (onshore, offshore, mountain, see table above) for the wind power investment.
-
Design two possible layouts for the wind farm. Each layout should take into account both the topological layout of the turbines, for example which direction they face and how they are sited with respect to each other, and the electrical layout, for example the main electrical components in the internal grid of the wind farm and the electrical connections between the turbines. Explain briefly why you have chosen the location and layouts, taking into account environmental aspects, grid connection aspects and economical aspects.
-
-
Assume that the wind speed data specific for your group has been measured at this location (This means that you do not have to look for a location whose wind conditions match the data you are given.), at a height of 10 meters. Wind coming from the North has an angle of 0°, East of 90°, South of 180° and West of 270°. Calculate the annual energy production of the wind farm for the two layouts and the two wind turbine models chosen in Section A, by making appropriate assumptions about the wind turbine availability, the wake effect between the turbines, the tower height and the roughness factor (It is possible to use an invalid “trick” here: take two locations and the same measured wind speed data, the location with the highest roughness factor will get higher wind speeds because of the logarithmic profile. This is not a valid argument for choosing a location. In short: do not choose a location because its roughness factor gives rise to higher wind speeds with the given data.).
-
Finally, for the rest of the study, choose a wind turbine from the two models you kept from Section A and a layout from the two you proposed and explain your choice.
Task C: Network Integration Issues
In this part, you are asked to choose a proper point to connect the wind farm to the grid. The grid that all teams will use for analysis of network integration is shown in the figure below (this is a schematic of the grid to which you will connect your wind farm). The data for each points to which the wind farm may be connected is given in the table below.
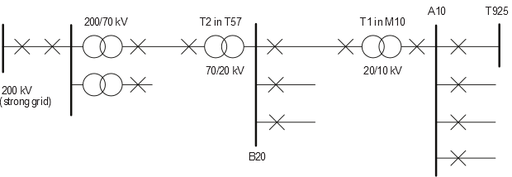
| Point Number | Connection Point | Short-circuit Capacity Sk (MVA) | Load/line/phase (A) | Number of lines |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | T925 | 450 | 150-370 | 2 |
| 2 | A10 | 800 | 150-390 | 4 |
| 3 | 20 kV side of T1 in M10 | 1000 | 130-345 | 2 |
| 4 | B20 | 1200 | 130-345 | 2 |
| 5 | 70 kV side of T2 in T57 | 1200 | 130-345 | 2 |
| 6 | 70 kV side of 200/70 kV transformer | 1700 | 120-325 | 1 |
| 7 | 200 kV side of 200/70 kV transformer | 2000 | 42-114 | 2 |
| 8 | Strong grid | – | 84-228 | 1 |
The following assumptions can be made for the calculations:
- the grid can be assumed to be purely inductive,
- load power factor can be assumed 0.9 inductive everywhere,
- the installed wind farm is controlled to keep a power factor equal to 1, voltage limits are +/- 10% for voltages above and including 70 kV, and -10%, +6% for voltage levels below 70 kV,
- the higher the short-circuit capacity of the connection point the higher the price for connection at this point.
Instructions
- Calculate the maximum capacity of a wind farm that can be connected to each of the connection points.
- Choose a location in the network where it is possible and most economically efficient to install your wind farm. Include all calculations and relevant curves which support your choice.
- What other issues need to be considered when choosing a connection point?
- What would happen if the wind farm was able to generate reactive power? Assume that the power factor of the wind farm is 0.95, and calculate the maximum capacity of the wind farm that can be connected in this case.
Notes and hints
- The voltage limits are given in terms of the nominal voltages, which are given by the transformer ratings.
- The network at every connection point can be represented by a Thévenin equivalent. The nominal voltages can be used for Thévenin voltages Uth.
- The load currents are given per line and per phase in table above. The total load is calculated approximately as \(S = n \sqrt{3} U_{th} I_{load}\) where n is the number of lines. From this \(P_{load}\) and \(Q_{load}\) are calculated as in Assignment 2.
- Also, the load currents given in the table above can take on all values in the given range, not just the extreme values.
- It is not enough to only consider the lowest load values.
- Using the simplifications above, the network can be simplified to a two node equivalent, and the voltage can be calculated using equation (5.29) from Static Analysis of Power Systems.
Task D: Economic Analysis
Instructions
- Describe, if any, the support scheme for wind power that is used at the location you chose.
- Calculate the life cycle costs of your project over a lifetime of 20 years. Include the cost of equipment, installation, maintenance, dismantling etc. in your analysis and make appropriate assumptions about the price of the power. Do not forget to include incomes from support schemes.
- Include a sensitivity analysis and summarize your findings.
Notes and hints
It is strongly advised to use the software RETScreen to do the economic analysis. RETScreen is a free Excel-based program and can be found at http://www.retscreen.net. It requires Windows and Excel. It is available in the student room at Teknikringen 33 (H building).
Task E: Discussion
Discuss the feasibility of your project.