by Annika Nilsson, Researcher
As we returned to Narsarsuaq after a week of fieldwork in communities of southern Greenland, the outer world came charging in: planes arriving with tourists on their way to various local excursions and high-profile news stories about US president Trump wanting to buy Greenland, including the aftermath of political reactions of uncomfortable surprise at such an absurd idea.
What people living in the villages and towns of Greenland think about this diplomatic exchange, we can only guess as it has not been visible in the reporting in international media. However, after talking to people and visiting places in southern Greenland, we know that opportunities to take part in important decisions are often lacking and that living conditions in small communities are often shaped by the priorities of others. The communication network is just one example. The Narsarsuaq airport in is on a US air force base, established during World War II and still serves a major communication hub for travels anywhere outside the region. The priorities of others also relate to mining, where Greenland has a long history of outsider’s attention because of its unique geology with a wealth of minerals. Past interests in southern Greenland included establishing a mine of cryolite, which was used for aluminum processing, in the small town Ivittuut. Today, we found this mine and the town deserted and the building in decay, though memories of past activities and their links to people in nearby places remain.
-
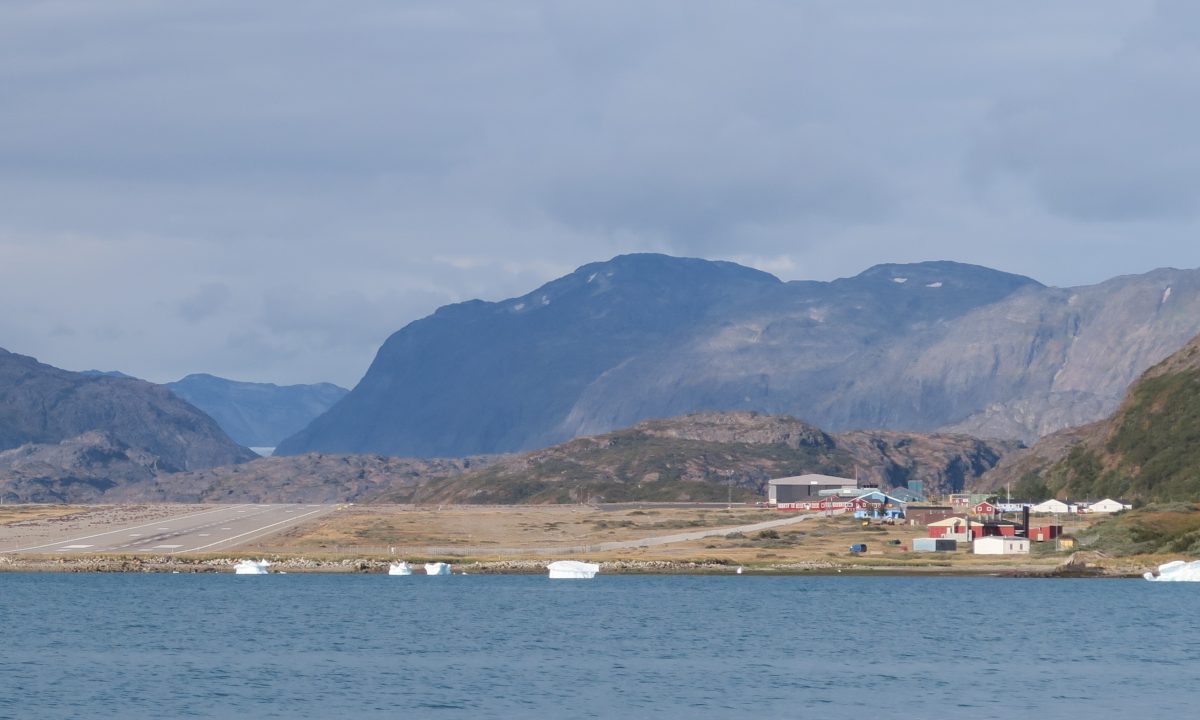

Approaching Narsarsuaq – Photo : Annika Nilsson
AMIDST MINING AND A POST-INDUSTRIALIZED FUTURE
Today’s focus is on the strategically important rare earth minerals that occur in the same ore as uranium at Kuannersuit (Kvanefjeld) by the small town of Narsaq. At the time of our visit, people were still waiting for a decision ‘from above’ about whether a mine would be opened. The discussion and the focus on mining had however already affected the town by creating social tensions between people who were either for or against this development. Some saw it as a source of new jobs as well as a base for a livelier service industry with restaurants, grocery stores and other facilities. As pointed out by one politician, it could also help pay for infrastructure in the form of roads that would connect nearby towns. For others, concerns about the impact of pollution raised major questions, especially if the mine would become detrimental to the rich fisheries in the area. A major hope was instead that the local fish processing plant would reopen. According to the local fishermen, shrimp was again abundant. The development of the local fish processing industry was however hampered by a changed structure of the Greenlandic fishery industry and what they saw as imposed bureaucracy and rules.
Some hopes were connected to increasing tourism but with a great concern that the transport infrastructure was insufficient. Most tourists appeared to stay around Narsarsuaq. To make tourism a viable industry also for other communities would require affordable and reasonably frequent boat transport or roads that connect at least some of the small towns in the area. The high cost of transport was a major concern for many people living in villages we visited.
Modern infrastructure is also about virtual communication routes. A visit to an internet café in Narsaq illustrated the cost of access to internet – a cup of tea and a blueberry muffin bought me 15 minutes of internet access. While some people have other access option, Greenland’s sea cable for internet was being repaired when we were visiting in August, limiting wire-carried internet access for private citizens in order to allow public institutions to continue to function. So, while international politicians and businesses discuss Greenland in ways that would have profound impact on the everyday lives in southern Greenland, people’s opportunities to get their own voices and priorities heard in the debate are circumscribed by costs and access to communication networks.
CREATING OPPORTUNITIES FOR ARSUK
Earlier in the week, we visited the settlement of Arsuk. We heard proud stories about how this town once had one of the world’s highest per capita income, when the cod was still plentiful. However, since the crash of the cod stock that previously brought riches and job opportunities to many Greenlandic communities, the outlook for economic opportunities has been bleak. With only four children left in the local school, no nearby access to health care and a harbor that the big ships pass by but do not stop at, several people expressed concern about the future of the community. However, there were also hopes from new sources of income. They included the possibility of selling carefully hand processed wool from muskox, which two women entrepreneurs were developing as a business. Once the 15 kg of fine wool prepared, it would be sent to Denmark for spinning and later sold to others who would knit garment for the Greenlandic market and possibly also for tourists. Arsuk is also home to a fish factory, whose owner expressed hopes that fish would again become plentiful.
While fishery is still part of everyday life in Arsuk, as it has been since the small town was funded in 1805, fishing is also circumscribed by other activities. An elder fisherman described how he had been ordered by a Danish Arctic Command vessel to cut his long line and get out of the way because the military was about to start an exercise in the area. Arsuk fishing activities have previously been hampered by military and industrial activities in the Arsuk fjord, which was home both to the Ivittuut mine, which has left lead pollution in the fjord, and to the Danish Grønnedal military station, both of which were geopolitically important during World War II. Thus, when we visited Ivittutt, Grønnedal, Arsuk and Narsaq, we were at the same time at the periphery of transport infrastructure and at the center of geopolitics.
-
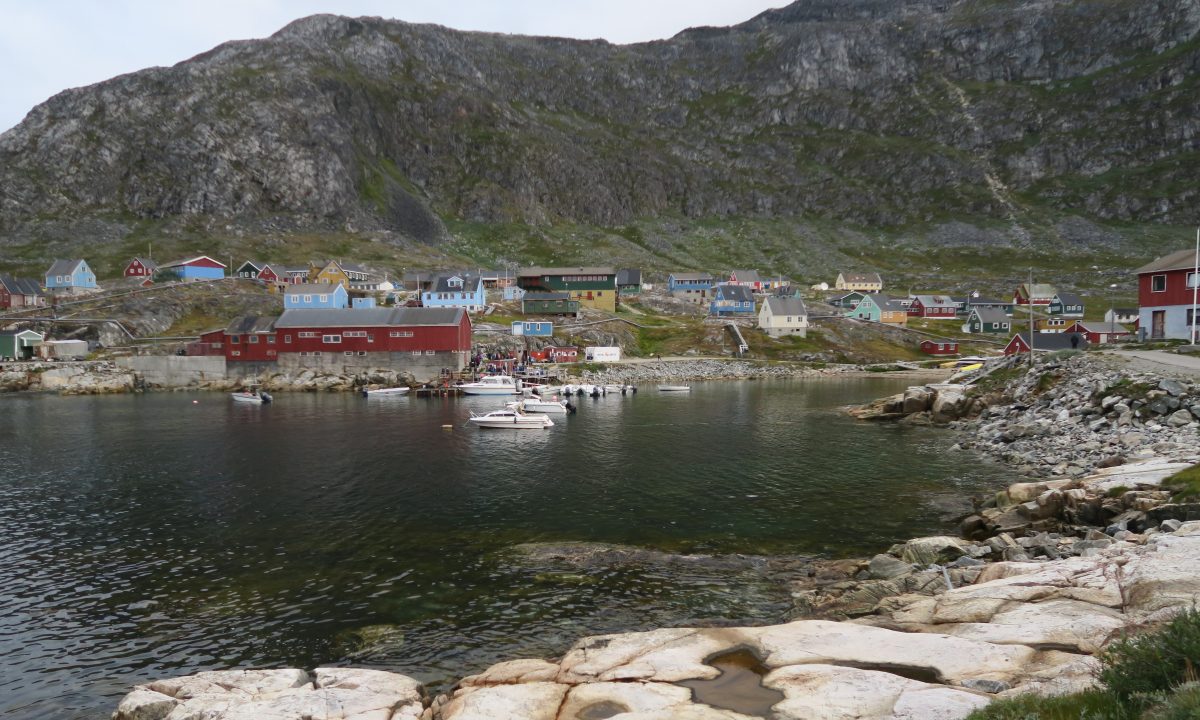

Arsuk harbor – Photo : Annika Nilsson
The Narsarsuaq airport may close in the future to be replaced by a regional airport near the town of Qaqortoq. However, the future is uncertain. It will depend not only on what might happen with the mine near Narsaq but also if climate change will have a positive impact on local fisheries. Indeed, in a scenario exercise with four young students, the military was highlighted as a major point of uncertainty when looking 20-30 years ahead in time. Although, when asked about what was most important, the focus was on education opportunities, the future of fisheries, and places to work. The voices of these young people and their peers need to be heard in the narratives about Greenland’s future.
*This post was initially published on the REXSAC blog. Many thanks to REXSAC for sharing this post with us.